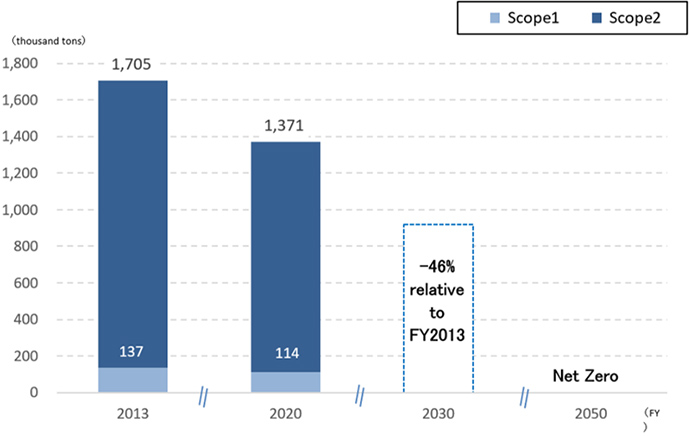
Goals toward carbon neutrality
With global environmental management theme, we have been constantly enhancing the environmental superiority of railways, which are more energy efficient and have less environmental impact than other modes of transportation, by proactively adopting energy-saving rolling stock and equipment. Additionally, we strive to further reduce CO2 emissions to achieve carbon neutrality in 2050. On the basis of the Japanese government's 2050 carbon-neutrality policy, JR Central and the JR Central Group aim to achieve net zero CO2 emissions in 2050 as well as reduce CO2emissions in FY2030 by 46% from FY2013 levels.
JR Central Group's CO2 emissions
Environmental superiority of railways
The problem of global warming is an issue that should be addressed on a global scale. As CO2 accounts for the largest emissions among greenhouse gases and is thus considered to have the largest impact on global warming, railways have the outstanding characteristic of being highly energy efficient compared to other transportation modes and having minimal adverse impact on the global environment. Railways account for only 7% of CO2 emissions despite undertaking 27% of Japan's overall passenger transport volume. Compared to an aircraft (B777-200), the Tokaido Shinkansen (Series N700 "Nozomi") consumes approximately one-eighth of the amount of energy per seat when traveling between Tokyo and Osaka and discharges about one-twelfth of the CO2 emissions, proving that the Tokaido Shinkansen has overwhelming environmental superiority. JR Central believes that having as many passengers as possible opt to use railway services, which have a smaller environmental impact than other modes of transport, will mitigate the load placed on the environment across the entire transportation sector and contribute to global environment preservation.
Distribution of Passenger Transportation Share, in terms of transportation volume, energy consumption, and CO₂ Emissions
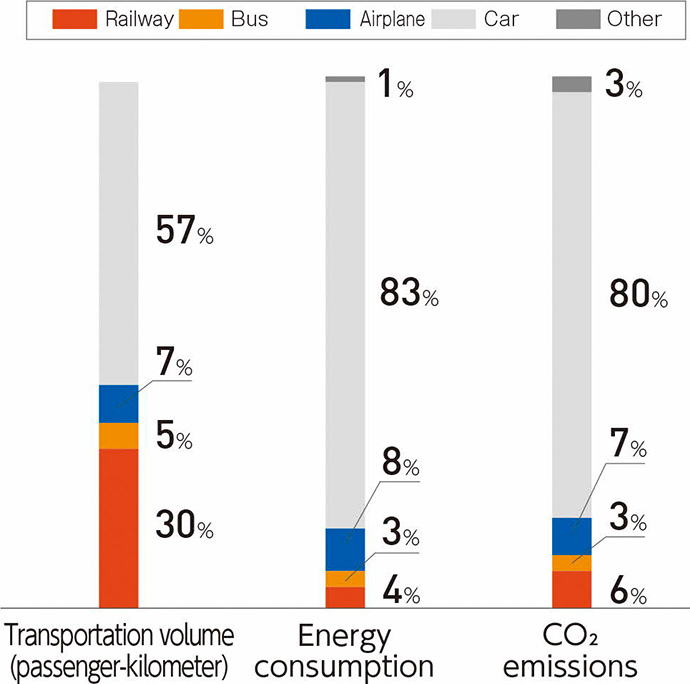
*The items in the breakdown may not add up to 100% due to rounding.
Source:
Handbook of Energy & Economics Statistics (2021) for transportation volume and energy consumption. 2021 data from the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Greenhouse Gas Inventory Office of Japan for CO2 emissions.
Comparison of the Tokaido Shinkansen and aircraft (between Tokyo and Osaka)
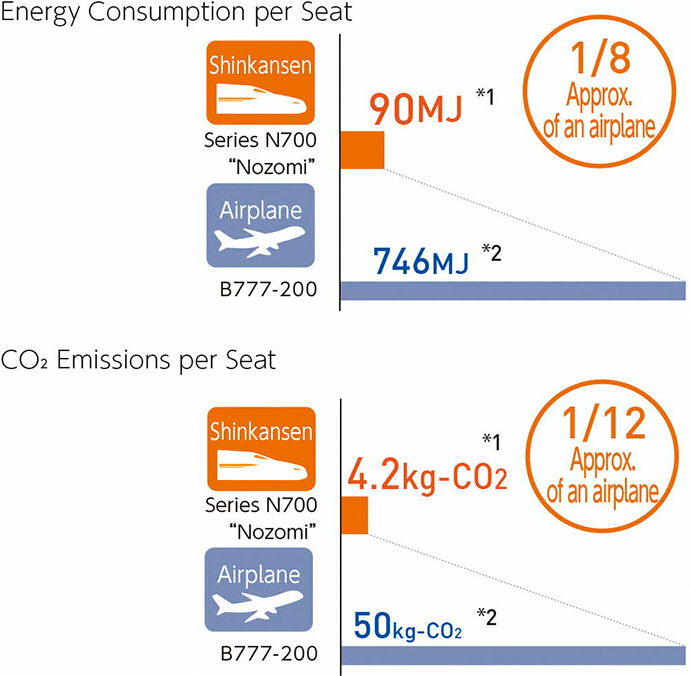
*1 Calculation based on running performance (by JR Central) of Series N700 "Nozomi" (Tokyo - Shin-Osaka).
*2 Calculated by JR Central for B777-200 (Haneda Itami/Kansai Airport) using ANA's "Annual Report 2011" for reference.
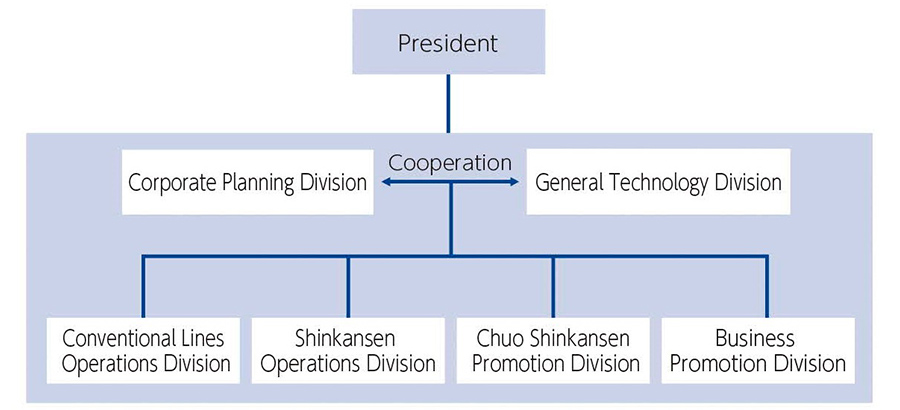
Promotion structure
JR Central promotes initiatives for global environment preservation through a structure headed by the President, under which the Corporate Planning Division and the General Technology Division, in charge of the management units and technology units respectively, cooperate to formulate policies for efforts to achieve carbon neutrality, resource recycling and biodiversity, as well as policies for technological development, and the Operations Divisions of the two railway businesses, the Chuo Shinkansen Promotion Division and the Business Promotion Division roll out the specific efforts.
Contribution to global environment preservation and the achievement of a decarbonized society
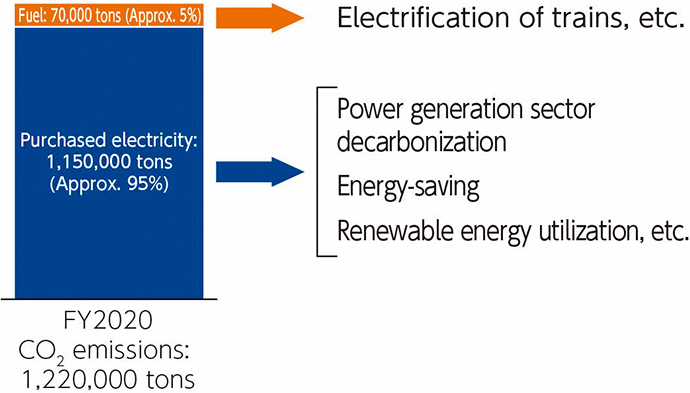
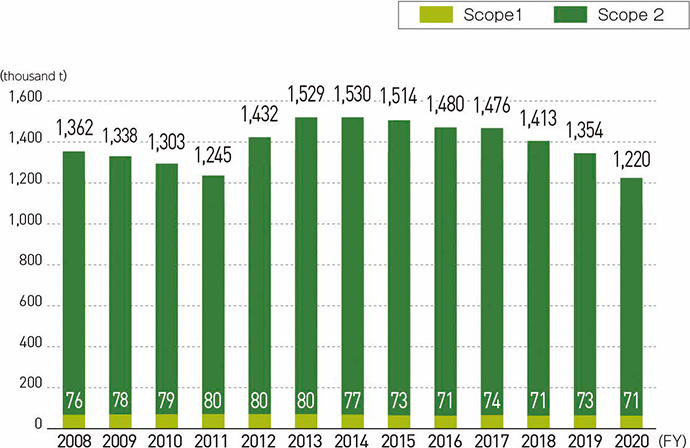
Of the 1.29 million tons of CO2 emitted by JR Central, approximately 95% is indirectly emitted through our use of electricity, while the remaining 5% is directly emitted through our use of fuels, etc. To address the 5% direct emissions from the use of fuels, we have introduced the Series HC85 with reduced environmental impact and will promote tests on biofuels. In addition, we have begun simulated driving tests combining railcar driving test equipment and hydrogen supply equipment to develop hydrogen-powered railcars and will continue to conduct research on battery railcars. To address the indirect emissions from the use of electricity, which account for the remaining 95% of the total, we will work to use renewable energy while making further energy-saving efforts, such as introducing additional energy efficient rolling stock, including the N700S and Series 315, and replacing frequency converters for the Tokaido Shinkansen one by one with types with lower power loss, in addition to promoting decarbonization efforts across the entire power generation sector in Japan. In May 2021, we endorsed the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD),* based on which we will consider strengthening our facilities against natural disasters through analysis of risks and opportunities related to climate change, so that we can ensure stable business operations over the long term. Furthermore, we will cooperate with external companies and organizations to contribute to the preservation of the global environment and the achievement of a decarbonized society by further enhancing the environmental superiority of railways through new technologies and initiatives that help reduce environment impact.
* Refer to URL below for information on the TCFD
URL https://global.jr-central.co.jp/en/company/ir/annualreport/_pdf/annualreport2024-20.pdf
Initiatives to reduce CO₂ emissions
Guidelines
Environmental Action Guidelines
JR Central has established a set of Environmental Action Guidelines consisting of the following seven items as part of its engagement in global environment preservation.
- [1]Provide comfortable transportation services to promote further use of railways, which offer superior global environment preservation
- [2]Promote technological development that contributes to global environment preservation
- [3]Use fuel and energy efficiently
- [4]Promote waste control and recycling
- [5]Appropriately manage chemical substances
- [6]Procure environmentally friendly goods and materials
- [7]Contribute to society and raise awareness for global environment preservation
Initiatives to reduce direct CO2 emissions
Hybrid-powered rolling stock
We have developed the new, hybrid-powered limited express Series HC85 as the successor to the Series 85 diesel railcars used for our limited express trains "Hida" and "Nanki" and introduced a total of 68 cars by July 2023. The Series HC85 achieves an approximately 30% reduction in diesel fuel consumption and CO₂ emissions and an approximately 40% reduction in NOx emissions in comparison to the Series 85 diesel railcars by making use of the power stored in the batteries when accelerating and stopping.
Comparison of diesel fuel consumption of conventional diesel cars (Series 85) and hybrid cars (Series HC85)
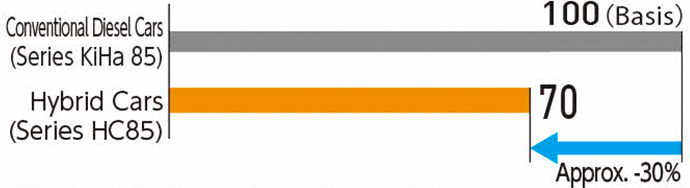
* Based on a simulated run from Nagoya to Toyama at the maximum speed of 120 km/h
Development of hydrogen-powered railcars and research on battery railcars
We have been working to develop hydrogen-powered railcars as a way of reducing CO2 emissions from diesel railcars to net zero. We plan to use hydrogen fuel cells or hydrogen engines as a power source instead of diesel engines, which use diesel as fuel, aiming to introduce a hydrogen-powered hybrid system that runs on electricity generated by such a power source and electricity from storage batteries. In order to test the performance of railcars powered by fuel cells or hydrogen engines and their suitability for our long-distance, nonelectrified routes with many mountainous areas, we began simulated driving tests combining railcar driving test equipment and hydrogen supply equipment in November2023. We have also been conducting research on battery railcars, which are equipped with a large running battery and can run on sections without overhead wires. To operate hydrogen-powered railcars, a stable and largescale supply of hydrogen is required. Therefore, in addition to developing hydrogen-powered railcars, it is necessary to establish a hydrogen supply chain that covers the transportation and storage of produced hydrogen and its filling, installation, and use in railcars. We are considering the optimal hydrogen supply chain for railways, using hydrogen carriers such as liquefied hydrogen and methylcyclohexane (MCH) for transporting and storing hydrogen. Moreover, we are also attempting to develop technology that has no precedent in Japan and overseas to extract hydrogen from MCH on railway cars.
Configuration of hydrogen-powered railcars
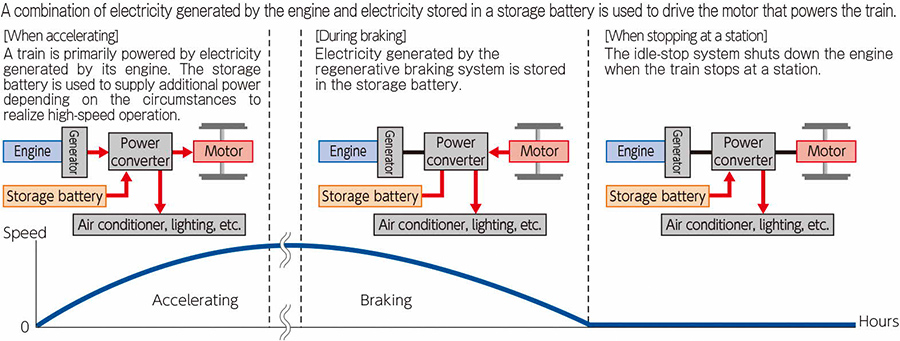
* Vehicle control device: A device that controls the operation of the electric motor by appropriately combining the output of fuel cells or a hydrogen engine and the charging and discharging of batteries
Biofuel tests
With regard to biofuels, we are conducting demonstration tests with the Railway Technical Research Institute and other JR companies for the introduction of biofuel under the "demonstration and evaluation of next-generation biodiesel fuel for railway vehicles," a technological development project of the Railway Technology Development and Promotion Framework by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
Initiatives to reduce indirect CO2 emissions
Energy-saving - Introduction of energy-conserving rolling stock -
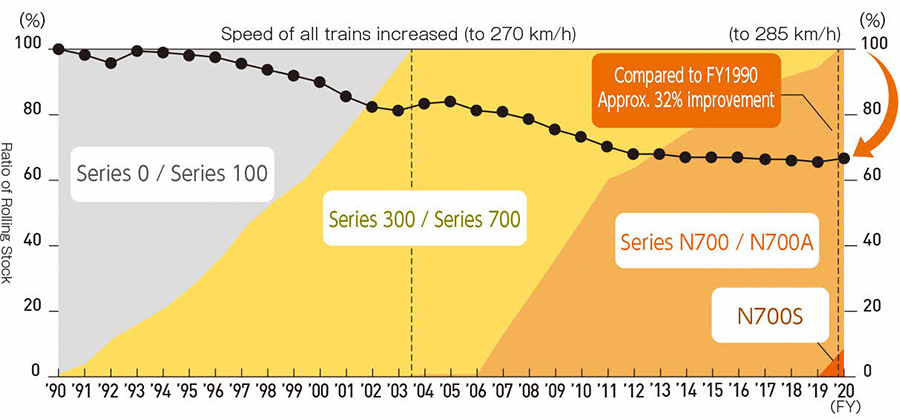
We are actively developing and introducing energy-conserving rolling stock in an effort to further reduce energy consumption on the Tokaido Shinkansen. We have been introducing the N700S since FY2020 to replace Series N700, with a plan to introduce 76trainsets by FY2028. The N700S consumes 7% less electricity than the N700A type*1 thanks to its silicon carbide semiconductor drive system, lighter car body, reduced running resistance, and other features. As a result, the unit energy consumption*2 as of the end of FY2023 decreased by approximately 32% compared to FY1990. Moreover, a function to maintain overhead line voltage, which has previously been performed by ground equipment, will be installed in N700S cars. This will make it possible to remove some of the substation functions, such as power compensators. When this function is implemented on all Tokaido Shinkansen trains, itis expected that CO2 emissions will be reduced by approximately 10,000 tons per year. We have also been striving to reduce the energy consumption of rolling stock on conventional lines. We have been introducing the new type commuter train Series 315 since FY2021 to replace Series 211, with a plan to introduce 352 cars by FY2025. With further improvements made in energy efficiency through the use of silicon carbide for the power converter, the Series 315 consumes approximately 35% less electricity than the Series 211.
Comparison of electricity consumption of electric railcars on conventional lines*

* Based on a simulated run from Toyohashi to Ogaki and from Nagoya to Nakatsugawa at the maximum speed of 120 km/h (rapid operation)
Comparison of electricity consumption by type of Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock
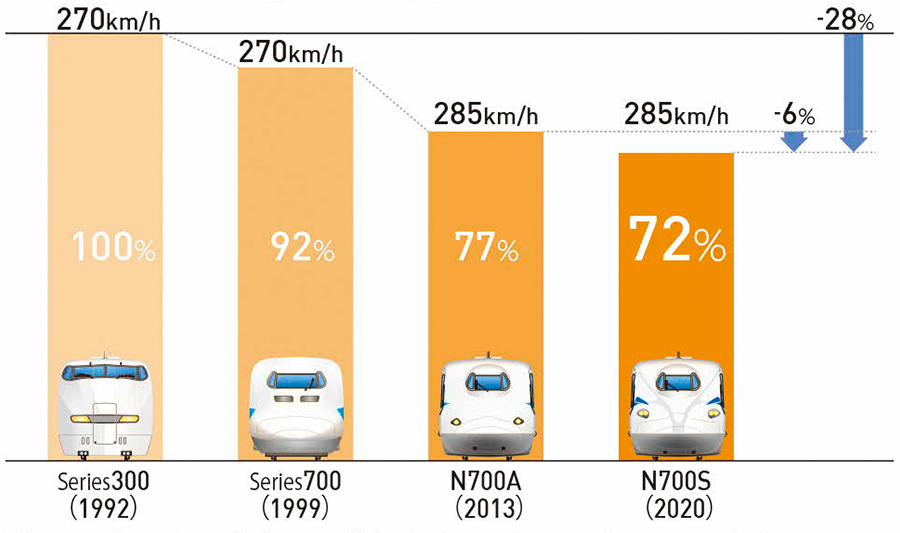
*1 Based on a simulated run from Tokyo to Shin-Osaka at the maximum speed listed above
*2 Figures in parentheses represent the year in which the series was introduced.
*3 Includes the effect of optimization of air conditioning control method
Trend of the ratio of Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock and unit energy consumption
Energy-saving - Facility improvement -
On the Tokaido Shinkansen, frequency converters are installed in sections east of the Fuji River to convert the 50Hz electricity received from the power company into the 60Hz electricity required for the Shinkansen to run. In the period from FY2021 to FY2027, two units of conventional, rotating-type frequency converters at Nishi-Sagami are being replaced with stationary type units with less power loss. In addition, the development of technology to suppress instantaneous large currents caused byground faults in overhead wires and to avoid overloads caused by train schedule disruptions, etc. has made it possible to make all frequency converters stationary. We plan to replace the twoTsunashima units with stationary types by the end of 2037. These replacements are expected to reduce electricity consumption by approximately 80 million kWh per year.
Renewable energy utilization
Of our facilities, the SCMAGLEV and Railway Park and the Hamamatsu Workshop have installed solar power generation systems. The systems generate power of approximately 450,000 kW per year each at the respective facilities. In addition, since FY2022, we have been working to achieve net zero CO2 emissions of electric railcars on the Taketoyo Line by purchasing and using FIT non-fossil fuel energy certificates*1equivalent to the approximately 2 million kWh of electricity used annually to operate trains on this line, from Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. Renewable energy utilization*1 The FIT non-fossil fuel energy certificate is a certificate of the non-fossil fuel energy value of the renewable electricity purchased under the FIT (Feed-in Tariff) system.
Initiatives on resource recycling
JR Central strives to recycle resources, promoting "threeRs" (reduce, reuse and recycle) initiatives, including reducing waste discharge from construction work, using rainwater, reusing uniforms, and recycling train tickets.
Recycled aluminum from Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock
Recycled aluminum made by removing impurities from scrapped Tokaido Shinkansen train cars is molded and processed for intended purposes and reused in a variety of products. The N700S car uses recycled aluminum for interior parts. Since we have ensured its reliability and quality as a car body material by establishing an aluminum sorting process, we have started using recycled aluminum in parts of the car body where strength is required. In addition to the bodies of Shinkansen trains, it has also been used as a construction material for the exterior of Gifu-Hashima Station, the station building of Shimoji Station on the Iida Line, the decoration of the souvenir shopping mall "Tokyo Gift Palette" at theYaesu North Exit of Tokyo Station, and the interior of the Shin-Yoko Gateway Spot waiting room at Sagami Railway and Tokyu Railways Shin-Yokohama Station. It has also been used for interior louvers jointly developed with DAIKEN Corporation and Sagamihara City, and as ceiling materials for "FUN+TECH LABO," an innovation creation promotion hub that we established in Sagamihara City. Furthermore, we are expanding the use of this recycled aluminum to include everyday products such as metal baseball bats for children, which we developed with Mizuno Corporation, and straws. Recycled aluminum from Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock can reduce CO2 emissions from the production process by 97% compared to manufacturing new aluminum, reducing environmental impact.
Manufacturing process and usage examples (metal bats and station building) of recycled aluminum from Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock

* Images in ② and ④ courtesy of SUS Corporation, and image of bats, of Mizuno Corporation

Interior louvers (FUN+TECH LABO)

Straws made from recycled aluminum from Tokaido Shinkansen rolling stock

Exterior image of Gifu-Hashima Station
Tokaido Shinkansen upcycling
We process Tokaido Shinkansen seats that have previously been discarded, and use them in an "upcycling" project to recycle them into new products. We also recycle seat fabric removed during vehicle inspection and maintenance work into products such as slippers.
Reuse of lead-acid batteries for level crossings
On conventional lines, we annually replace a certain number of lead-acid batteries installed in level crossing facilities as a backup power supply in case of power outages. We began in June 2023 to test a process for recycling and reusing used lead-acid batteries at some level crossing facilities, using Rent Corporation's lead-acid battery recycling technology. If the required performance and durability are confirmed through the tests, we plan to gradually introduce recycled lead-acid batteries, which will contribute to not only the reduction of waste but also the reduction of CO2 emissions. We note thatCO2 emissions from recycling lead-acid batteries are more than 90% less than those from manufacturing them.
Sustainability initiatives at hotels
JR Tokai Hotels Co., Ltd. is striving to reduce the amount of plastic products it provides, such as by providing paper straws and take-out tableware made from alternative materials. In addition, Hotel Associa Takayama Resort has registered as Takayama City's "Hida Takayama SDGs Partner" and is contributing to the reduction of food waste by developing Hamburg steak that uses scraps of Hida beef and menu items that incorporate locally sourced ingredients.
Sustainable public procurement
JR Central implements a green procurement policy, prioritizing the procurement of environmentally friendly materials. To this end, we have established the JR Central Green Procurement Guidelines to enhance coordination with our suppliers, and work with them to contribute towards global environment preservation.
URL https://global.jr-central.co.jp/en/company/material_procurement/_pdf/green_guide_line.pdf
Conservation of biodiversity and coexistence with local communities
In order to reduce the impact of our business activities on ecosystems and contribute to local communities, we are working to conserve biodiversity in cooperation with external companies and organizations. For example, in order to further promote the conservation of the natural environment of the Southern Alps, we engage in the following initiatives to support local residents' efforts to conserve alpine plants and improve forests.
Conservation of alpine flora
In Japan's Southern Alps, there has been the issue of loss of flower fields due to deer depredation and sediment discharge, among others. In Nagano Prefecture, the Southern Alps Counter-Depredation Association has been implementing measures to protect alpine flora by installing deer-proof fencing and capturing Japanese deer, among other measures. In March 2022, JR Central entered into a Biodiversity Partnership Agreement with the Southern Alps Counter-Depredation Association and Nagano Prefecture to support part of the expenses necessary for alpine plant conservation activities conducted by the Association, thereby contributing to the expansion of the protected area. In addition, our employees take part in the work to install deer-proof fences.
Forest maintenance
In Fujikawa Town and Hayakawa Town in Yamanashi Prefecture and Oshika Village and Ina City in Nagano Prefecture, which are centered around the Southern Alps UNESCO Eco Park, JR Central is supporting the efforts of the local communities to maintain forests. We are also working to set up a zero-carbon day, a day when trains will operate with net zero CO2 emissions, by using the amount of CO2 absorption certified by each prefecture through this forest maintenance support to offset CO2 emissions from train operations on the Minobu and Iida Lines. We aim to continue the effort to "protect, use, and nurture" the natural environment of the Southern Alps as a whole, together with people in the local communities involved.
Initiatives on compliance with laws and regulations
As part of our efforts to preserve the global environment, we annually conduct compliance surveys of all workplaces to ensure compliance with various environmental laws and regulations and appropriately manage chemical substances, etc. Furthermore, we conduct internal audits to confirm the compliance status of each workplace and provide feedback on the audit results in an effort to ensure thorough compliance.
Management of chemical substances
Based on the PRTR system* under the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Law), we report the amount of emissions and transfer of relevant substances and manage those substances appropriately. Furthermore, while we had been using oil-based paint containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for full bodypainting of trains on the Shinkansen and conventional lines, we introduced the country's first water-based paint coating robot for the Shinkansen in our Hamamatsu Workshop in2017, enabling environmentally friendly water-based painting. We also introduced the country's first water-based paint coating robot for the front of trains on conventional lines in the Nagoya Workshop in 2020, enabling water-based painting of some bodies.
* A system whereby business operators identify the amount of chemical substances that may be harmful to human health or the ecosystem and that are released from their business sites into the environment (air, water and soil) and are transferred outside of business sites as part of waste, and report it to the national government. The government then tabulates and discloses the amounts released and transferred based on such reported data and estimates.

Train body painting
Measures against pollution
As measures against water contamination and air pollution, we strive to prevent pollution by installing devices to treat waste water left after washing vehicles and burners that reduce the generation of NOx and by conducting regular measurement. In addition, as measures against soil contamination, should any substances exceeding the standard value set be detected in soil surveys conducted at the time of landform changes or land sale, we submit a report to the relevant organizations and take appropriate measures as instructed by laws and regulations and the administrative authorities.
Cooperation with external entities
Environmental Partnership Organizing Club (EPOC)
EPOC is a group that was established in 2000 mainly by the industry sector in the Chubu region, with the aim of building a sustainable economy and society by leveraging the environmental achievements of companies. (Please see EPOC's website for more details.) We joined EPOC in FY2002 and are currently involved in the operation of the organization as a core company. We will continue to contribute to global environment preservation through EPOC in cooperation with member companies among others.
Enhancement of PR activities to highlight railway's environmental superiority

PR poster to highlight railway's environmental superiority
Toward the realization of a decarbonized society, the JR Group and the Japan Private Railway Association are working together to implement PR activities to promote the use of railways, a relatively lowcarbon mode of transportation, and to foster social understanding. In implementing PR activities, each company uses a common logo and slogan to introduce the efforts each railway operator is making to reduce CO2 emissions.
Environment-related data
Activity status and environmental accounting for FY2023
The investments, costs, and their principal effect involved in environment preservation activities during FY2023 are estimated as listed below.
Environmental accounting
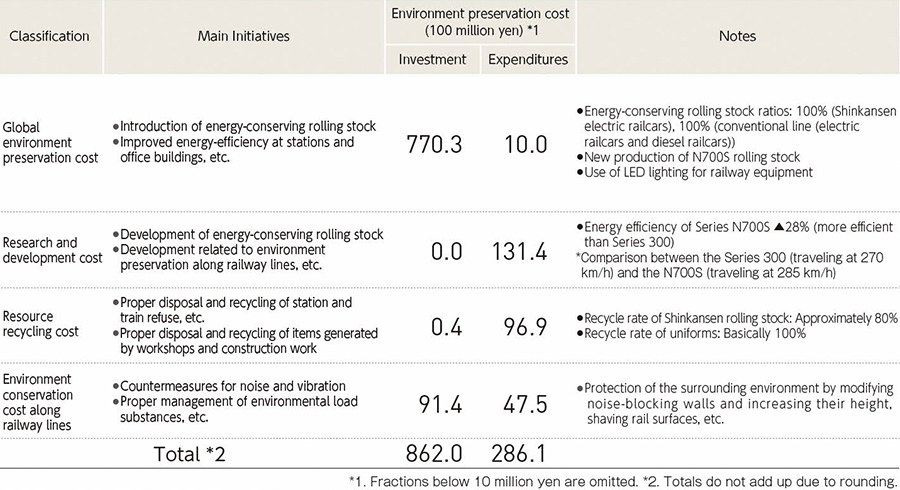
*1. Fractions below 10 million yen are omitted.
*2. Totals do not add up due to rounding.
[Approach to environment preservation cost]
● Compilation is applicable only to JR Central.
● The applicable period is April 1, 2023 to March 31, 2024.
● "Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2005," a publication of the Ministry of the Environment, was consulted with regard to aspects of style.
● Depreciation is not included in the calculations for expenditures.
● In the event of multiple-purpose expenditures, the full amount with greater environment preservation effect is included in the calculation.
Environmental load in business activities
The main resources and energy consumed as well as waste generated in JR Central's business activities during the year FY2023 are as shown below.
INPUT/OUTPUT
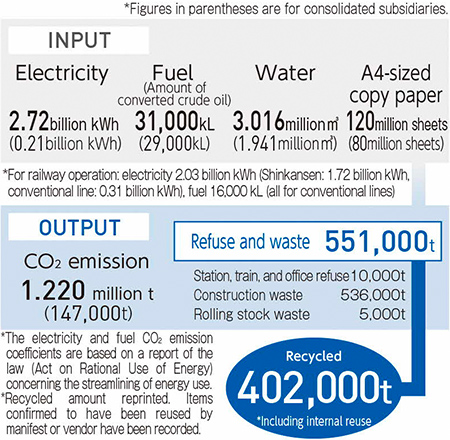
CO2 emissions
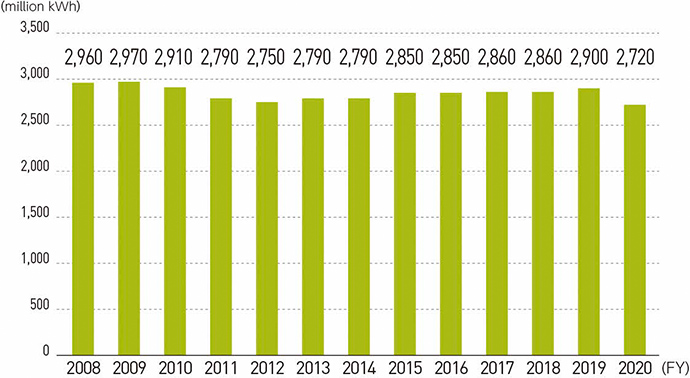
Electricity consumption
Carbon intensity
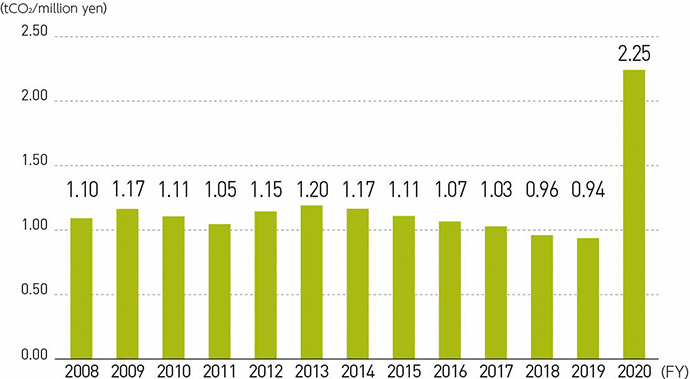
Note: Carbon intensity rose in FY2020 as operating revenues (non-consolidated) decreased significantly due to the impact of COVID-19.
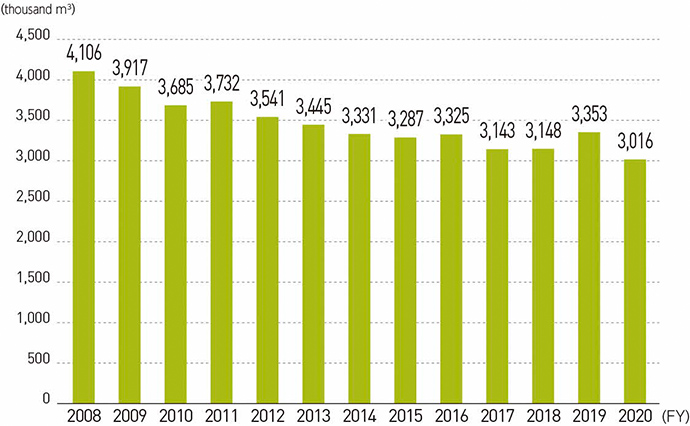
Amount of water used